In today’s technological landscape, the contrast between QR Codes and linear barcodes stands out as a key factor in business decisions, offering two distinct methodologies for data encoding and management.
The QR Code
QR code stands for “Quick Response” and was developed by the Japanese company Denso Wave in 1994. It was created in response to the need for an encoding system that could hold more information than traditional barcodes and could be easily decoded using mobile devices.
The origins and first use
The QR code was first conceived by Masahiro Hara, an engineer at Denso Wave, a subsidiary of the Japanese automobile company Denso Corporation. It was developed to be a form of two-dimensional barcode that could contain more information than linear barcodes.
Initially, the QR code was used in the Japanese automotive industry to keep track of components during the manufacturing process. Later, it was adopted in other industries, such as marketing, advertising, public transportation and more.
Current Uses
- Marketing and Advertising: The QR code is widely used in marketing and advertising to provide quick access to additional information, promotions, discounts, promo videos, etc. Consumers can simply scan the code with their smartphones to access the content.
- Mobile Payments: In many regions of the world, QR codes are used to make mobile payments. People can use their financial services apps to scan a store’s QR code and make a cashless payment.
- Inventory Tracking and Management: QR codes are used to track and manage inventories in various industries, such as logistics and transportation. They can be used to identify and track the movement of goods and packages along the supply chain.
- Interactive Content: QR codes can be used to provide interactive content in various contexts, such as museums, art exhibitions and historical monuments. Users simply scan the code to access additional information, audio guides, virtual tours, and more.
Evolution over Time
- Standardization and Popularity: In recent years, QR codes have become increasingly popular and standardized. Major mobile operating systems, such as iOS and Android, have integrated QR scanning capabilities directly into their cameras, making it easier for users to access QR content.
- Technological Innovations: Innovations in the field of QR codes have been ongoing, such as the introduction of dynamic QR codes that allow users to change the content of the code without having to create a new code. There are also QR codes with custom designs and advanced tracking and analysis capabilities.
In conclusion, the QR code has evolved significantly since its creation in the 1990s, and has become a versatile tool used in a wide range of applications, to provide information, to simplify transactions, and to improve interactivity among individuals and the world around them.
The linear barcode
- Invention: The barcode concept was first developed in the 1940s. One of the earliest designs was developed by Bernard Silver and Norman Joseph Woodland, who obtained a patent in the United States for an automatic identification system based on barcodes in 1949. This system used bars and spaces of varying widths to represent numbers.
- Development of the UPC Barcode: In the 1960s, the linear barcode system was further developed and refined. In 1974, the Universal Product Code (UPC) barcode was introduced in the United States as a standard for product identification in supermarkets. The first product to be scanned with a UPC code was a pack of mint gum on June 26, 1974.
- Worldwide Diffusion: In the following years, the linear barcode became a global standard for product identification. It has been adopted in various sectors besides retail, such as logistics, health care, manufacturing, and more.
- Variations and Standardization: Over time, several variants of linear barcodes have been developed to meet the specific needs of different industries and applications. However, a UPC code remains among the most common and recognizable codes.
- Technological Advances: Despite the wide adoption of linear barcodes, there have also been continuous technological developments and improvements in the field of automatic identification. Still, linear barcodes remain widely used today, although two-dimensional barcodes such as QR codes are becoming increasingly popular for their more complex information storage capabilities.
Comparison between the old linear bar code and the new, dynamic QR Code
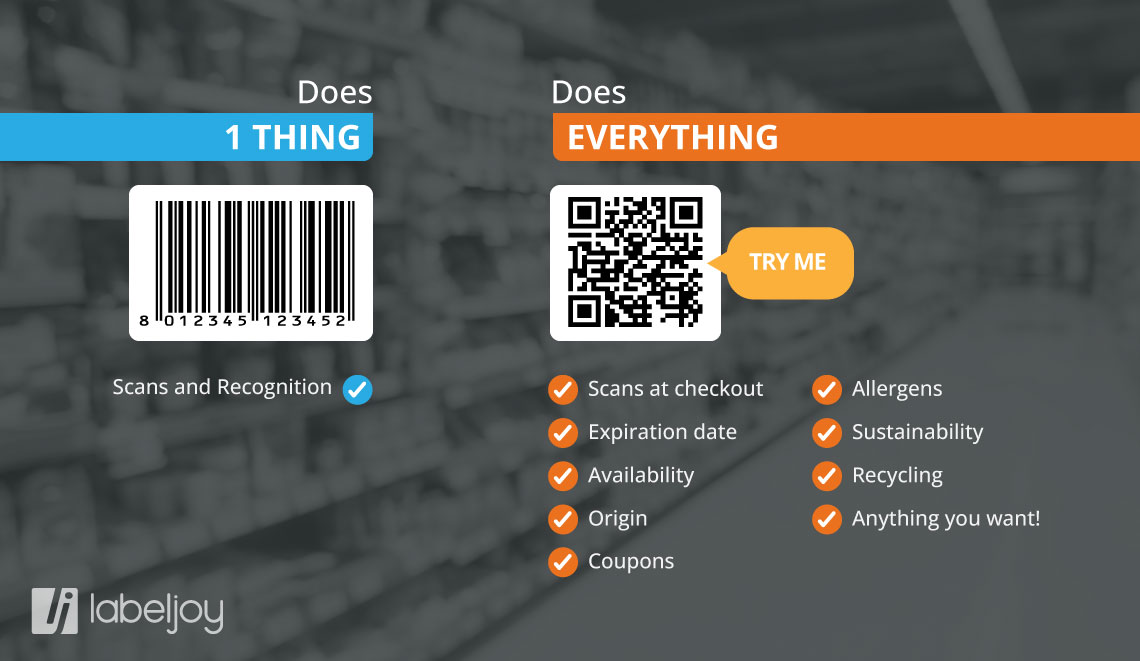
Infographic comparing QR Codes and linear Bar Codes
1. Dimensional Structure
QR Code
It is a two-dimensional code, which means it contains information in two directions: horizontal and vertical. It can store a large amount of data, including text, links, numbers, and more.
Linear Code
It is a one-dimensional bar code, represented by horizontal parallel lines. It can contain less information than a QR code and is usually used to encode numbers or alphanumeric codes.
2. Storage Capacity
QR Code
Has significantly higher storage capacity than linear bar codes. It can contain more than 7,000 numeric characters or more than 4,000 alphanumeric characters.
Linear Code
Has limited storage capacity compared to QR codes. It can usually contain less than 30 numeric or alphanumeric characters.
3. Scanning
QR Code
Can be read from any angle, which makes scanning faster and more flexible. It can also recover data even if part of the code is damaged or obscured.
Linear Code
Requires scanning in a linear fashion and must be aligned correctly to be read properly. It is more sensitive to errors due to damage or darkening.
4. Usage
QR Code
It is commonly used for a wide range of applications, such as web links, contact information, digital business cards, mobile payments, etc.
Linear Code
It is often used for more specific purposes, such as product tracking, barcodes of goods in stores, identification codes in logistics, etc.
5. Design
QR Code
Has a dot-matrix design and can contain information in the form of square modules.
Linear Code
Has a linear design with various bar widths and spaces.
Conclusions
In summary, while both types of bar codes have their own specific applications, QR codes offer greater versatility and storage capacity than linear codes.
